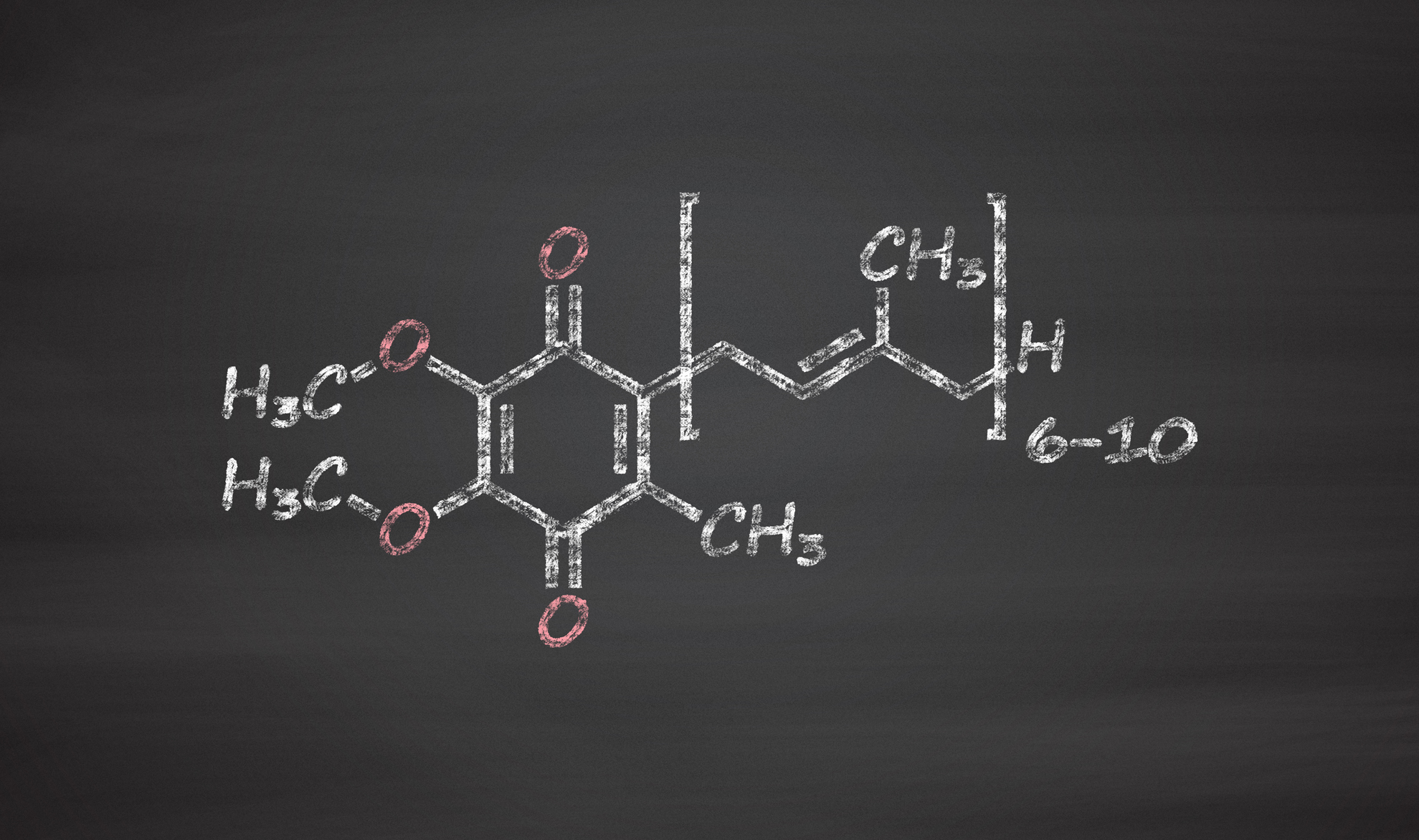
COQ10
Coenzyme Q10, CoQ10 for short, is a multi-talented nutrient that is no stranger to the supplement industry, and for good reason. It is also referred to as “ubiquinone” for its ubiquitous presence in virtually every cell of the human body. Functioning as an antioxidant and contributing to cellular health, CoQ10 is also required to convert carbohydrates and fats into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is the workhorse of usable cellular energy which is needed to perform almost every key bodily function, thereby contributing to heart, brain, muscle, and immune system health. Before we get into the nuances of CoQ10, let’s discuss what a coenzyme is and why CoQ10 is worth supplementing in your diet.
To understand the nature of coenzymes, it is important to have a grasp of what an enzyme is. Simply put, an enzyme is a protein which acts as a catalyst to bring about a specific biochemical reaction. Each enzyme is highly specific, meaning it will facilitate the process of only one reaction, (of hundreds of thousands), in the body. These compounds are responsible for speeding up virtually every biochemical reaction that takes place within our cells. Vital for life, enzymes play a major role in functions as important as digestion, tissue formation, energy production, and heartbeat. Sometimes enzymes cannot complete a reaction on their own, and this is where coenzymes go to work.
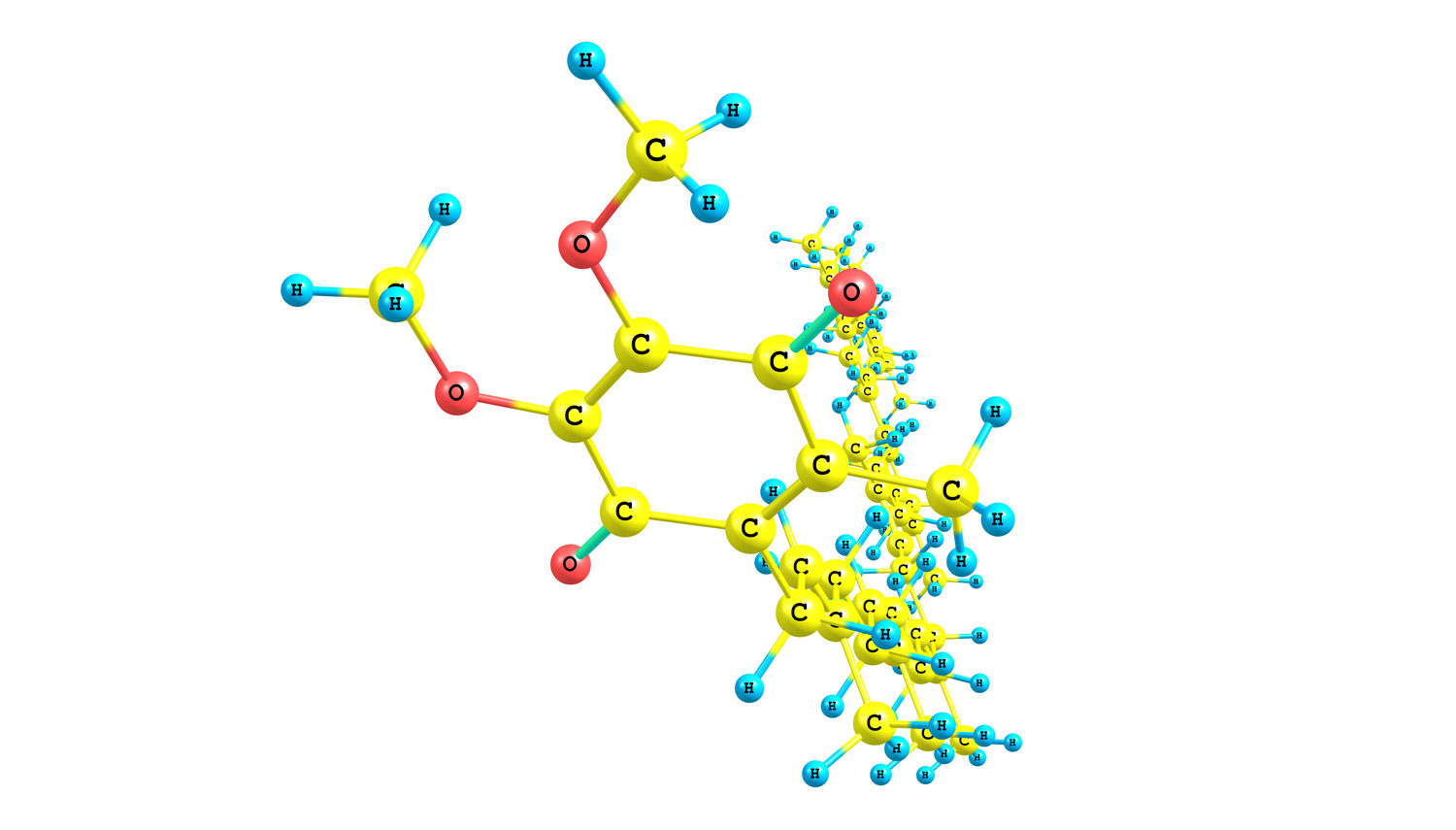
CoQ10 is a required element in the production of ATP. As we know, the production of ATP benefits everything from building and preserving muscle mass to aiding in the regulation of appetite and body weight. Another highly valuable function of CoQ10 is its role in reducing the cellular damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are formed constantly throughout the body and their production increases when we are more active and consume more oxygen. These molecules cause serious damage to cell structure, called oxidative stress, that can ultimately lead to disease and contribute to the functional declines that come with aging. Natural CoQ10 levels within our tissue have been known to decline with age, and a deficiency is thought to contribute to a decline in energy metabolism and a weakening of organs and skeletal muscle.
Cognitive function is another area where CoQ10 has a positive effect. Mitochondria, the cellular organelles responsible for converting nutrients into ATP, exist in higher densities within brain cells than in most other cells in your body. By sustaining healthy levels of CoQ10, which protect and propel our mitochondria, brain cells endure less damage from oxidative stress. The effects of oxidative stress on brain cells can lead to symptoms of slow mental processing, poor memory, and a “mental fog” sensation. CoQ10 not only slows the deterioration and aging process of our brain’s cellular structure, but it supports the normal function of brain cells as well.

While the amount is small, there are a variety of foods where CoQ10 can be found naturally. Meats such as grass-fed beef, free-range chicken, and rainbow trout contain some of the highest concentrations. Vegetables, fruits, and nuts, including broccoli, strawberries, cauliflower, and pistachio nuts, contain small amounts of CoQ10 as well. Supplemental sources can be preferable for consuming consistent and adequate amounts of this valuable nutrient.
While we are admittedly biased, two highly effective supplements which contain CoQ10 are Wilderness Athlete Hydrate & Recover and Energy & Focus. Support your cellular health and much more with Coenzyme Q10 today!